What is Well-being?
Well-being is a positive state experienced by individuals and societies. Similar to health, it is a resource for daily life and is determined by social, economic and environmental conditions. Well-being encompasses quality of life and the ability of people and societies to contribute to the world with a sense of meaning and purpose. -World Health Organisation
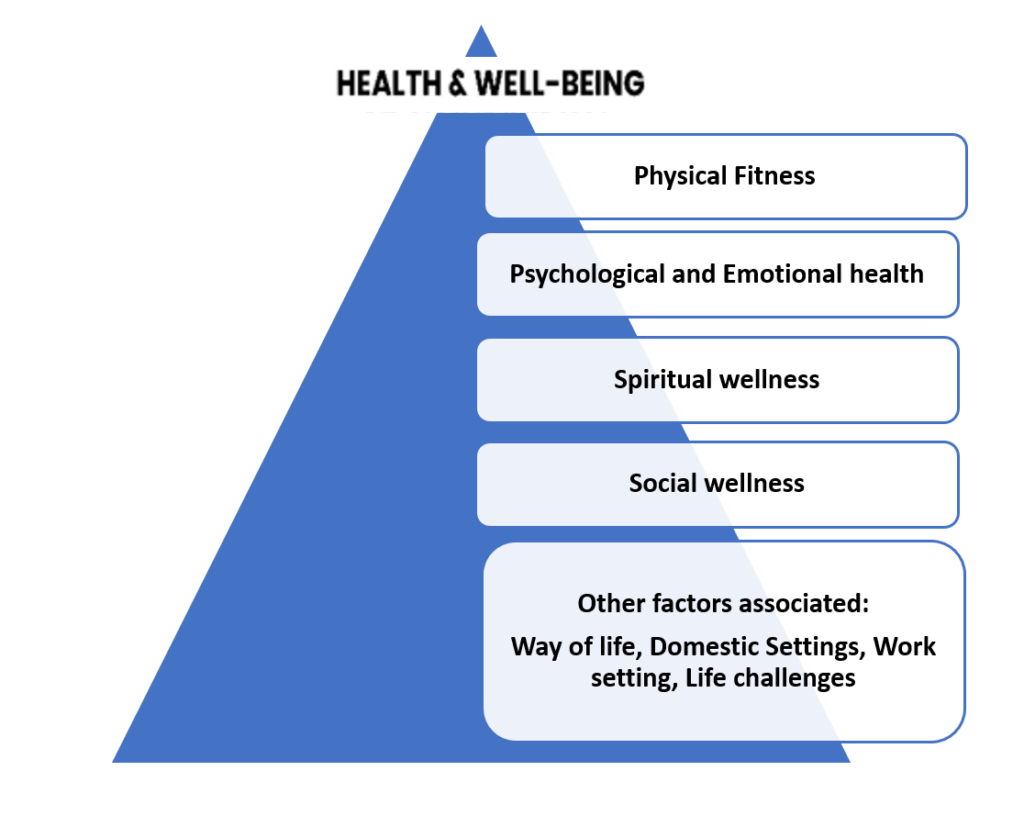
Figure: Factors associated with health and well-being
Components of wellbeing
“No health without mental health” – World Health Organisation
Spiritual
Finding purpose, meaning, and connection to something greater than oneself.
Social
Building and aintaining healthy relationships and a supportive community.
Economic
Financial stability and access to resources for a comfortable life.
Ecological
Living in harmony with the environment and promoting sustainability.
Physical
Maintaining a healthy body through exercise, nutrition, and rest.
Psychological
Mental clarity, resilience, and the ability to cope with stress.
Emotional
Understanding, expressing, and managing emotions effectively.
Determinants affecting well-being
Determinants influencing well-being include inadequate nutrition, physical inactivity, excessive alcohol intake, tobacco/substance abuse, social disconnectivity, poor work-life balance, prolonged stress, financial instability, inaccessible health care services, exposure to trauma, etc. Any factor, condition or behaviour that hampers an individual’s physical, social, psychological or emotional health, contributes to vulnerable and poor well being.
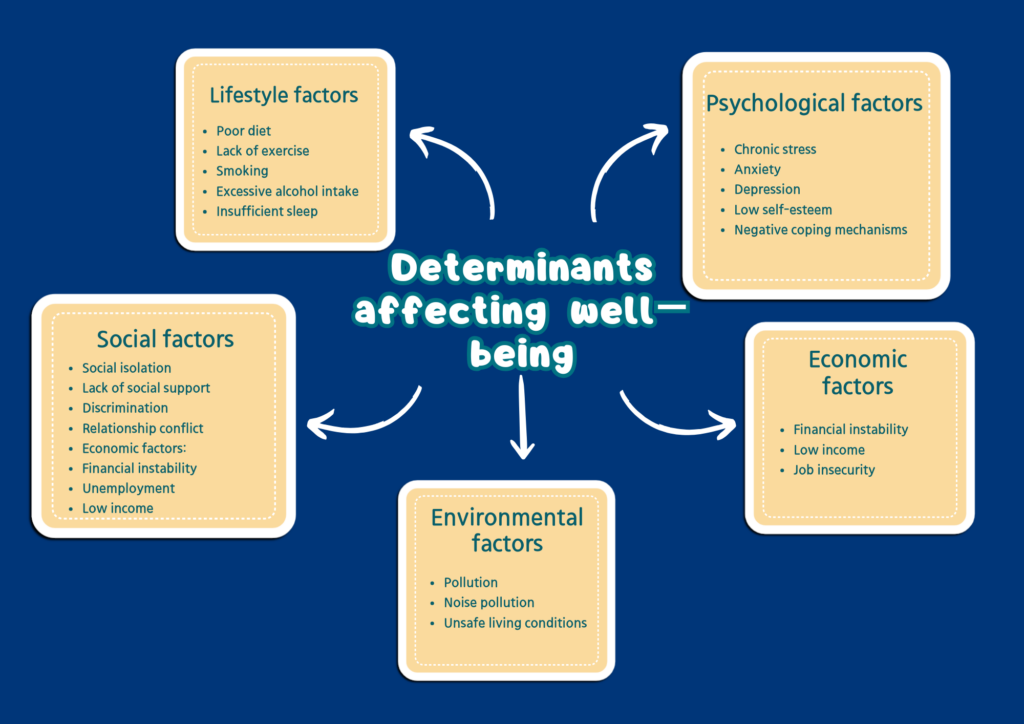
Research and reports reveals:

Youth Well-being
Youth well-being is progressively an essential part of the concept of well-being. An urgent need for interventions and policies has been expressed to address the psychological aspects of young individuals (9).
Research indicates:






