What is Well-being?
Well-being is defined as a positive state encountered by an individual comprising quality of life and abilities to contribute to development. It is a valuable resource influenced by societal dynamics, economic factors and environmental conditions (1). It is a multidimensional notion, comprising objective measure including quality of life and subjective measures comprising psychological, cognitive, social aspects (2).
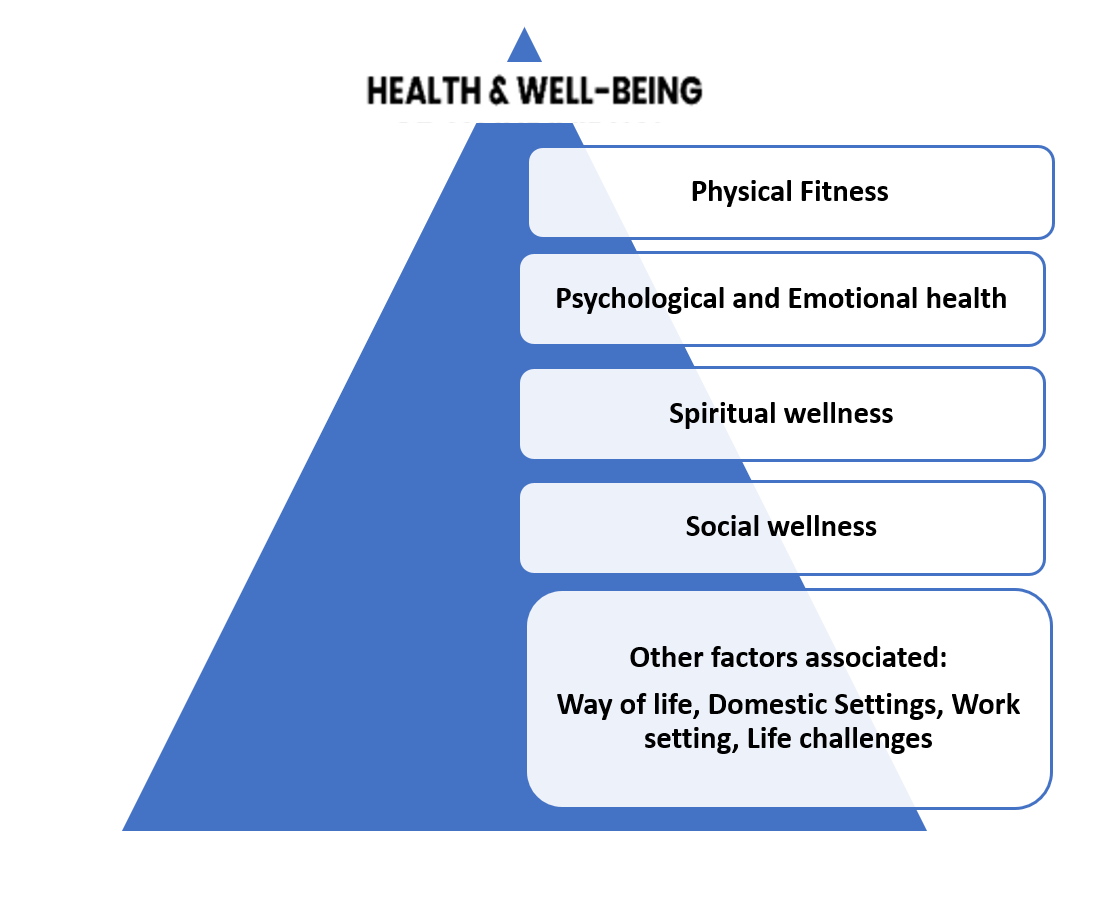
Figure: Factors associated with health and well-being
Advancing in the arena of well-being is essential as it pertains to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (1).
Major Threats to Well-being
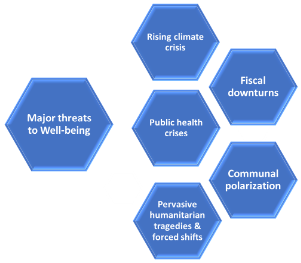
Figure: Major threats to Well-being (4)
Research and reports reveals:

- Individuals with schizophrenia or any other severe mental health diseases often die 10 to 20 years earlier as compared to general population (3)
- A recent study on university students showed a linkage between stress, depression, anxiety and unhealthy eating practices (5)
- Over 46.6 million adults in United States, had mental illness (6)
- General usage of social media is related with poorer psychological well-being which further effects physical health and well-being (7)
- Lonesomeness and social separation have effects on overall health in addition to well-being (8)
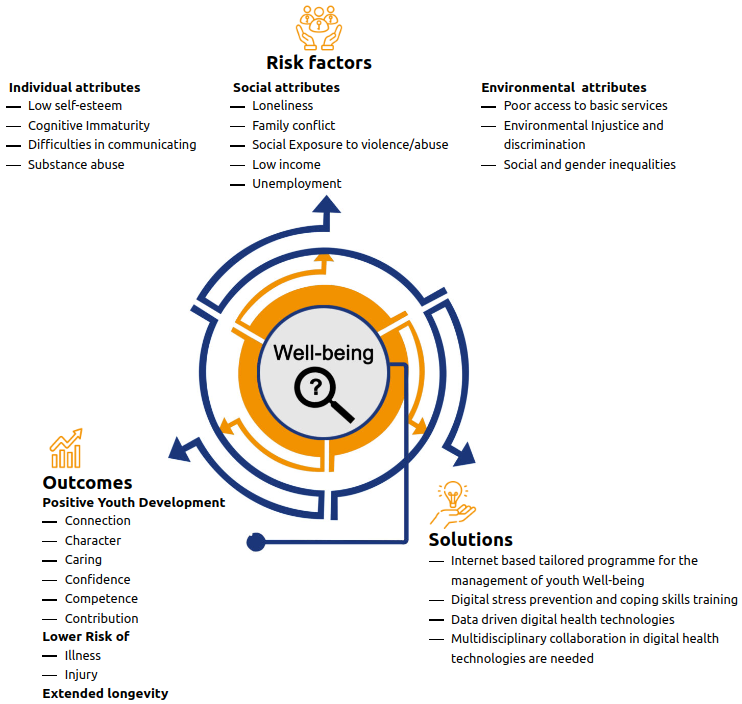
Youth Well-being
Youth well-being is progressively an essential part of the concept of well-being. An urgent need for interventions and policies has been expressed to address the psychological aspects of young individuals (9).
Research indicates:

Sources
- Trudel-Fitzgerald C, Millstein RA, von Hippel C, Howe CJ, Tomasso LP, Wagner GR, et al. Psychological well-being as part of the public health debate? Insight into dimensions, interventions, and policy. BMC Public Health 2019 Dec 19;19(1):1712 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-8029-x] [Medline: 31856772]
- O’Reilly M, Svirydzenka N, Adams S, Dogra N. Review of mental health promotion interventions in schools. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2018 Jul;53(7):647-662 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.1007/s00127-018-1530-1] [Medline: 29752493]
- Kris-Etherton PM, Petersen KS, Hibbeln JR, Hurley D, Kolick V, Peoples S, et al. Nutrition and behavioral health disorders: depression and anxiety. Nutr Rev 2021 Feb 11;79(3):247-260 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa025] [Medline: 32447382]
- Liverpool S, Mota CP, Sales CMD, Čuš A, Carletto S, Hancheva C, et al. Engaging children and young people in digital mental health interventions: systematic review of modes of delivery, facilitators, and barriers. J Med Internet Res 2020 Jun 23;22(6):e16317 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.2196/16317] [Medline: 32442160]
- India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative Mental Disorders Collaborators. The burden of mental disorders across the states of India: the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2017. Lancet Psychiatry 2020 Feb;7(2):148-161 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30475-4] [Medline: 31879245]
- India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative Mental Disorders Collaborators. The burden of mental disorders across the states of India: the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2017. Lancet Psychiatry 2020 Feb;7(2):148-161 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30475-4] [Medline: 31879245]
- Ramón-Arbués E, Martínez Abadía B, Granada López JM, Echániz Serrano E, Pellicer García B, Juárez Vela R, et al. Conducta alimentaria y su relación con el estrés, la ansiedad, la depresión y el insomnio en estudiantes universitarios [Eating behavior and relationships with stress, anxiety, depression and insomnia in university students.]. Nutr Hosp 2019;36(6):1339-1345 [FREE Full text] [doi: 10.20960/nh.02641] [Medline: 31657605]
- Luthra S, Agrawal S, Kumar A, Sharma M, Joshi S, Kumar J. Psychological well-being of young adults during COVID-19 pandemic: Lesson learned and future research agenda. Heliyon. 2023 May 4.
- Courtney K. Blackwell, Maxwell Mansolf, Phillip Sherlock, Jody Ganiban, Julie A. Hofheimer, Charles J. Barone, Traci A. Bekelman, Clancy Blair, David Cella, Shaina Collazo, Lisa A. Croen, Sean Deoni, Amy J. Elliott, Assiamira Ferrara, Rebecca C. Fry, Richard Gershon, Julie B. Herbstman, Margaret R. Karagas, Kaja Z. LeWinn, Amy Margolis, Rachel L. Miller, T. Michael O’Shea, Christina A. Porucznik, Rosalind J. Wright; on behalf of the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes Research Program, Youth Well-being During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pediatrics April 2022; 149 (4): e2021054754. 10.1542/peds.2021-054754
- Chandra R, Kumar S, Supehia S, Das A, Agarwal D. Psychological distress and well-being assessment among Indian people during COVID-19 pandemic. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Apr;11(4):1341-1347. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1203_21. Epub 2022 Mar 18. PMID: 35516666; PMCID: PMC9067216.
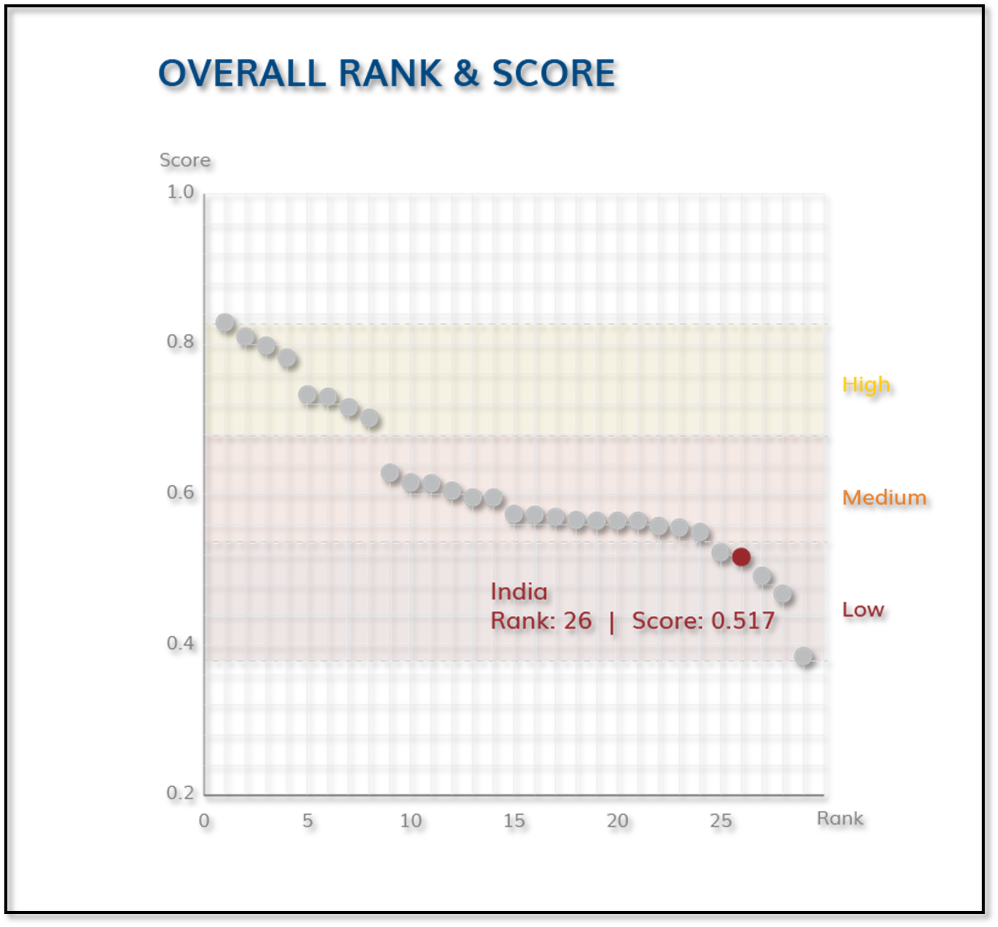
India Country Profile: Youth well-being Index

Overall Rank and Score of India Country Profile: Youth wellbeing Index
References
- Sharma R. Global Youth Wellbeing Index [Internet]. McCormick KR, editor. www.iyfnet.org. International Youth Foundation; 2017 [cited 2023 Jun 27] p. 1–147. Available from: https://www.youthindex.org/
- World Health Organization. Promoting well-being [Internet]. www.who.int.2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/activities/promoting-well-being
- Naci H, Ioannidis JP. Evaluation of wellness determinants and interventions by citizen scientists. Jama. 2015 Jul 14;314(2):121-2. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.6160.7
- Strine, T.W., Chapman, D.P., Balluz, L.S. et al. The Associations Between Life Satisfaction and Health-related Quality of Life, Chronic Illness, and Health Behaviors among U.S. Community-dwelling Adults. J Community Health 33, 40–50 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-007-9066-4
- Strine, T.W., Chapman, D.P., Balluz, L. et al. Health-related quality of life and health behaviors by social and emotional support. Soc Psychiat Epidemiol 43, 151–159 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-007-0277-x
- Helliwell J, Layard R, Sachs J. World Happiness Report 2018 [Internet]. 2018. Available from: https://s3.amazonaws.com/happiness-report/2018/WHR_web.pdf
- Lakshmanasamy T. Subjective well-being in India: Socioeconomic and demographic determinants and differentials. Indian Journal of Mental Health. 2021;8(1):70-83. https://www.academia.edu/download/70952764/IJMH_SWB_in_India.pdf
- Chan WY, Sloan J, Chandra A. Promoting youth well-being through health and education: Insights and opportunities. RAND Corporation. 2019;5:1-03. https://www.wise-qatar.org/app/uploads/2019/09/rr.5.2019-web.pdf
- Full report | The Global Youth Wellbeing Index [Internet]. www.youthindex.org. Available from: https://www.youthindex.org/full-report