Study Aim
The aim of the study is to design, develop and pilot test a digital health platform to enhance student well-being.
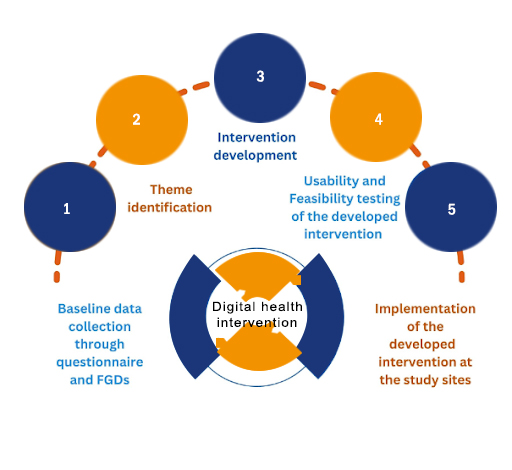
Study Design
Mixed methods
(Qualitative and quantitative research method)
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on numeric and unchanging data and detailed, convergent reasoning rather than divergent reasoning. It deals in numbers, logic, and an objective stance.
Study Sites

Panimalar Medical College Hospital & Research Institute
Varadharajapuram, Poonamallee, Chennai, Tamil Nadu- 600123, India

Parul Institute of Public Health, Parul University
P.O. Limda, Waghodia, Vadodara, Gujarat- 391760, India

Government Doon Medical College
Patel Nagar, Dehradun, Uttarakhand- 248001, India

Foundation of Healthcare Technologies Society
321, 322 & 323 Third floor, Somdatt Chamber 2, 9 Bhikaji Cama Place, New Delhi, Delhi 110066, India
Study Methods
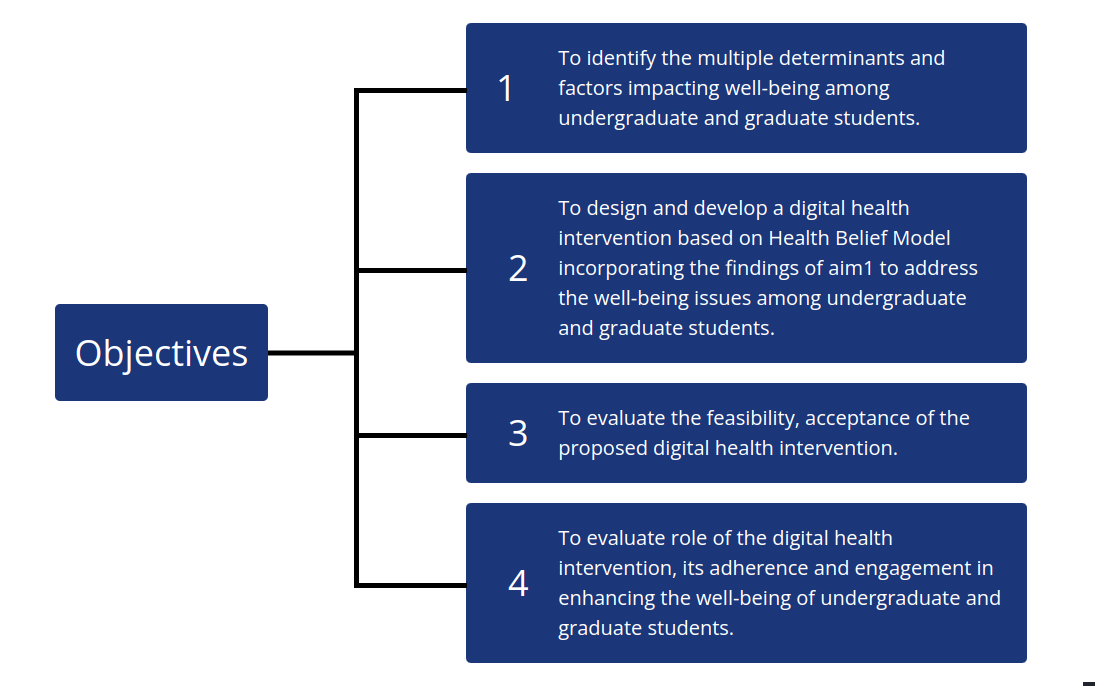
Objectives
Methods
Outcome
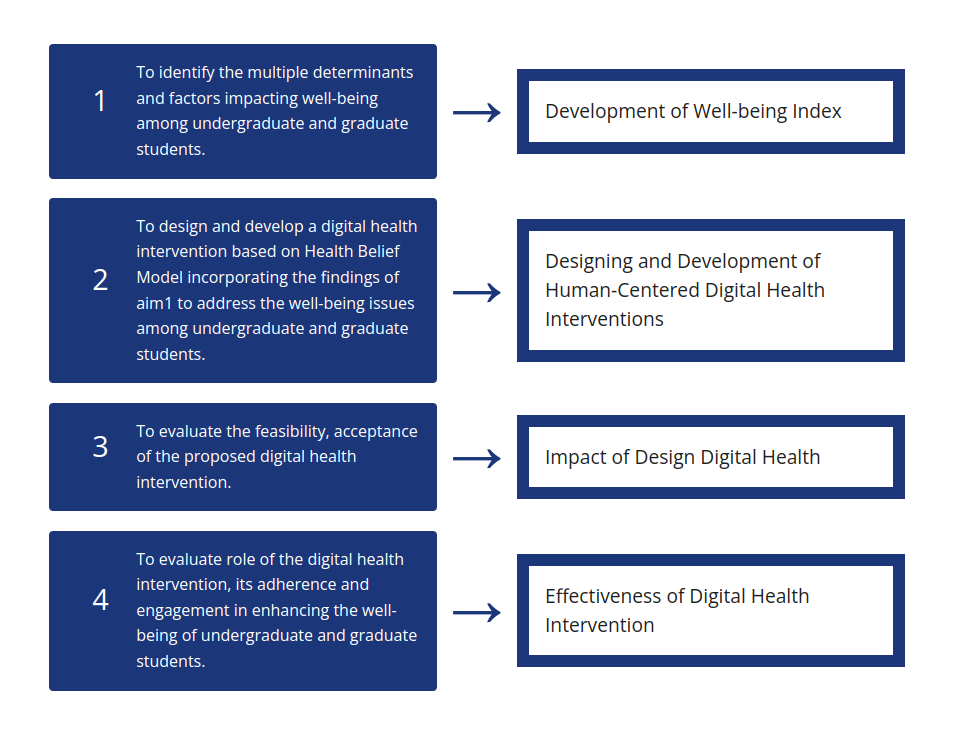
To identify the multiple determinants impacting dimensions of well-being among
undergraduate &graduate students
Pre-defined questionnaire & validated tools to identify multiple determinants affecting the
well-being.
Development of Well being Index
To design and develop an interactive digital intervention for various
dimensions of well-being
Determinants from the objective 1 & 2 FGDs per site.
Design development of Human Centered Digital Health Interventions
To evaluate the feasibility and acceptance of digital health intervention and
their role to enhance the well-being of undergraduate and graduate students.
A randomised control trial: Intervention group-mobile/ web- based platform with tailored
well-being related education.
Acceptability of Digital Health
To evaluate the role of digital health intervention ,its adhereance and
engagement in enhancing the well-being of undergraduate and graduate students.
A randomised control trial: Intervention group-mobile/ web- based platform with tailored
well-being related education.
Effectiveness of Digital Health Intervention
Study Methodology
Visual Representation of Study Objectives and Outcomes
Sample Size
| College | Sample Size |
|---|---|
| Panimalar Medical College Hospital & Research Institute, Varadharajapuram, Poonamallee, Chennai, Tamil Nadu | 2500 |
| Parul University, Post Limda, Waghodia, Vadodara, Gujarat | 2500 |
| Government Doon Medical College, Patel Nagar, Dehradun, Uttarakhand | 1020 |
Study Eligibility
Inclusion criteria
- The eligible study participants will be 18 years older
- Enrolled in one of the colleges: Government Doon Medical College (GDMC), Patel Nagar, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, Panimalar Medical College Hospital & Research Institute, Varadharajapuram, Poonamallee, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, and Parul University, Post Limda, Waghodia, Gujarat
- Having access to Wi-Fi/internet-enabled devices and being willing to give consent to participate in the study
Exclusion criteria
- Participants less than 18 years older
- Not enrolled in the institute
- Involuntary consent will be excluded from the study
Proposed Outcomes
The study will help to identify multiple determinants affecting well-being of undergraduate and graduate students.
Explore the role of digital health interventions to enhance the good health and well-being of undergraduate and graduate students.
Help in designing and developing individualized, tailored and interactive internet-enabled digital health interventions to manage well-being of undergraduate and graduate students.
Intervention
Study Variables
The General Self [Internet]. Fu-berlin.de. 2023 [cited 2023 Jun 30]. Available from:
http://userpage.fu-berlin.de/health/engscal.htm
Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (MSPSS) | Measures Library [Internet]. Miami.edu. 2023 [cited 2023 Jun 30]. Available from: https://elcentro.sonhs.miami.edu/research/measures-library/mspss/index.html
Cohen S. PERCEIVED STRESS SCALE [Internet]. 1994. Available from:
https://www.mindgarden.com/documents/PerceivedStressScale.pdf
Ethical Approval
Panimalar Medical College Hospital & Research Institute, Varadharajapuram, Poonamallee, Chennai, Tamil Nadu Ethical committee approved the study in April 2023 with approval number PMCHRI-IHEC-071.
Parul University Institutional Ethical committee for Human Research(PU-IECHR), registered under DCGI, GoI (Reg.No. ECR/702/Inst/GJ/2015/RR-21) approved the study in December 2022, with approval number PUIECHR/PIMSR/00/081734/5310.
Government Doon Medical College, Patel Nagar, Dehradun, Uttarakhand Institutional Ethical committee approved the study on April 2023 with approval number GDMC/IEC/2023/36.